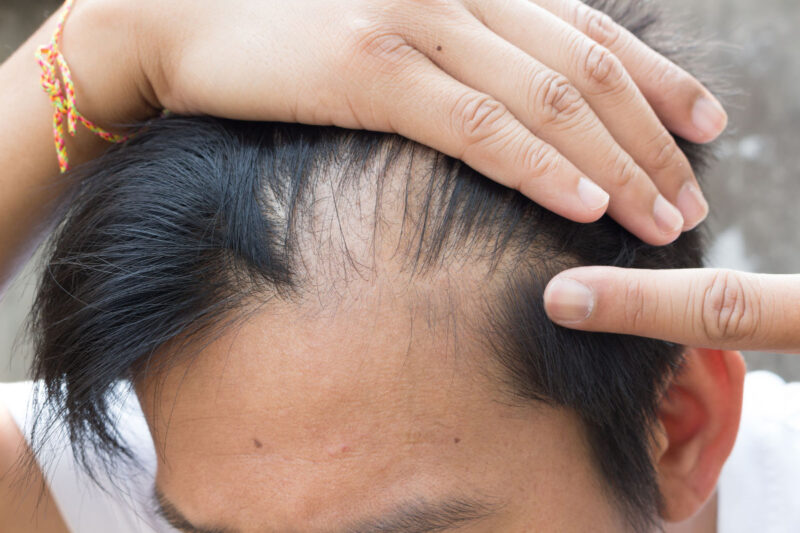
Male Pattern Baldness (MPB) is a condition that affects millions of people around the world and has been linked to genetics. While attempts have been made in its treatment, it remains largely mysterious.
In this article, we will be exploring the complex genetics at work behind MPB as well as looking into some potentially effective treatment approaches. We will also delve into how these treatments can help manage or even halt the progression of hair loss caused by MPB.
So join us as we unravel the mysteries surrounding male pattern baldness and discover potential ways to address it!
Male Pattern Baldness: An Overview
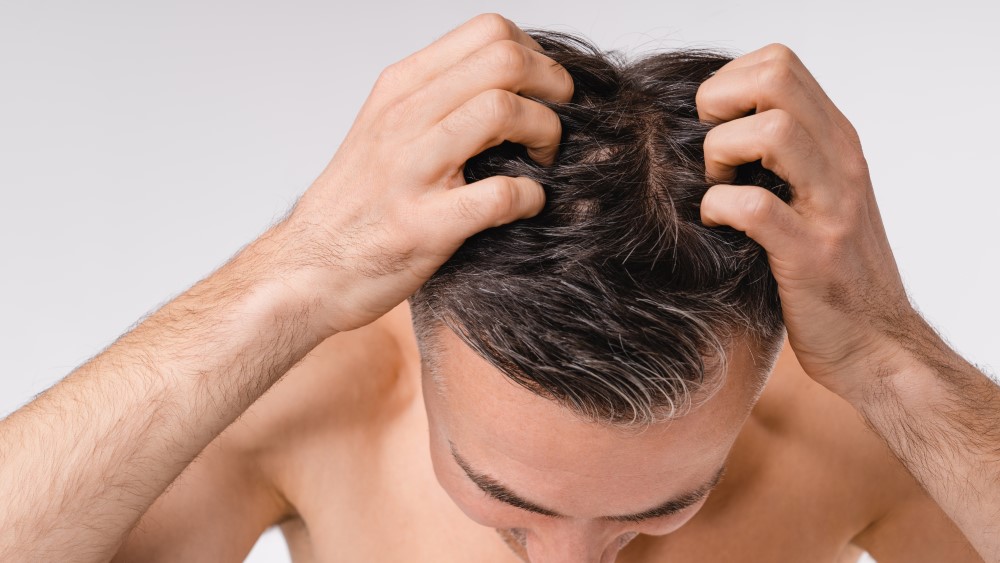

Male pattern baldness (MPB), also known as androgenic alopecia, is a common condition affecting millions of men around the world. It is characterized by receding hairlines, thinning hair on the crown of the head, and eventually complete baldness in some cases.
While MPB has been observed for centuries, our understanding of its genetics and treatment approaches is just beginning to be unraveled. The diagnosis of MPB typically involves physical examination as well as laboratory testing to rule out other causes such as hormonal imbalances or autoimmune diseases. Genetic studies have revealed several genes associated with male pattern baldness that could play an important role in determining susceptibility to this condition.
Research into potential treatments includes topical medications, laser therapy, dietary supplements, and even surgical procedures designed to restore hair growth. Ongoing research will likely continue to uncover new developments in understanding male pattern baldness along with more effective ways of treating it in the future; however, it remains an area ripe for further exploration given its complexity and impact on those affected by it worldwide.
Unraveling the Genetics of Male Pattern Baldness
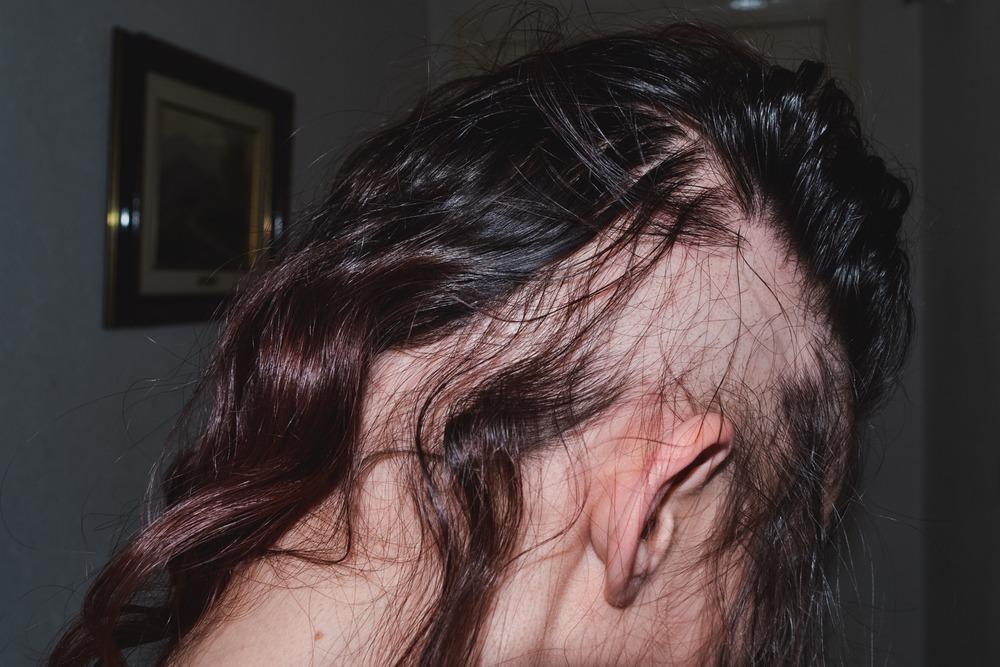

Male pattern baldness (MPB) is a common condition that affects millions of men, leading to thinning hair and the eventual loss of the majority of scalp hairs. While the cause of MPB has long been considered genetic, recent studies have shed light on the specific genes involved and how they interact with environmental factors to produce this condition.
In this article, we will explore the genetics behind male pattern baldness and some possible treatment approaches for those looking to manage their symptoms. The primary gene linked to male pattern baldness is called Androgen Receptor (AR). This gene regulates how cells respond to hormones such as testosterone, causing them to become more active when exposed.
This increased activity can lead to changes in follicle size and shape, creating an ideal environment for receding hairlines or complete hair loss. Additionally, other genes associated with MPB may influence the onset age and severity of symptoms.
Although there are no known cures yet for male pattern baldness due to its complexity in genetics those affected by it need to understand their options when it comes to managing their symptoms. Various treatments exist including medications such as Minoxidil which can help slow down hair loss; laser therapy which helps stimulate new growth; topical solutions like shampoos containing natural ingredients such as caffeine or saw palmetto extract; even surgical options like Hair Transplantation can be used if desired though they come at a certain cost both financially and physically speaking.
With these treatments available individuals must seek advice from doctors before deciding on any particular course so they fully understand all implications before proceeding. In conclusion, understanding the genetic makeup behind MPB provides us with a better way forward when seeking out treatment options.
Hopefully, further research into its complexities will give us additional insight into potential ways forward making sure everyone affected receives proper care while hopefully finding one day a cure that works best for them specifically.
Treatment Approaches for Male Pattern Baldness
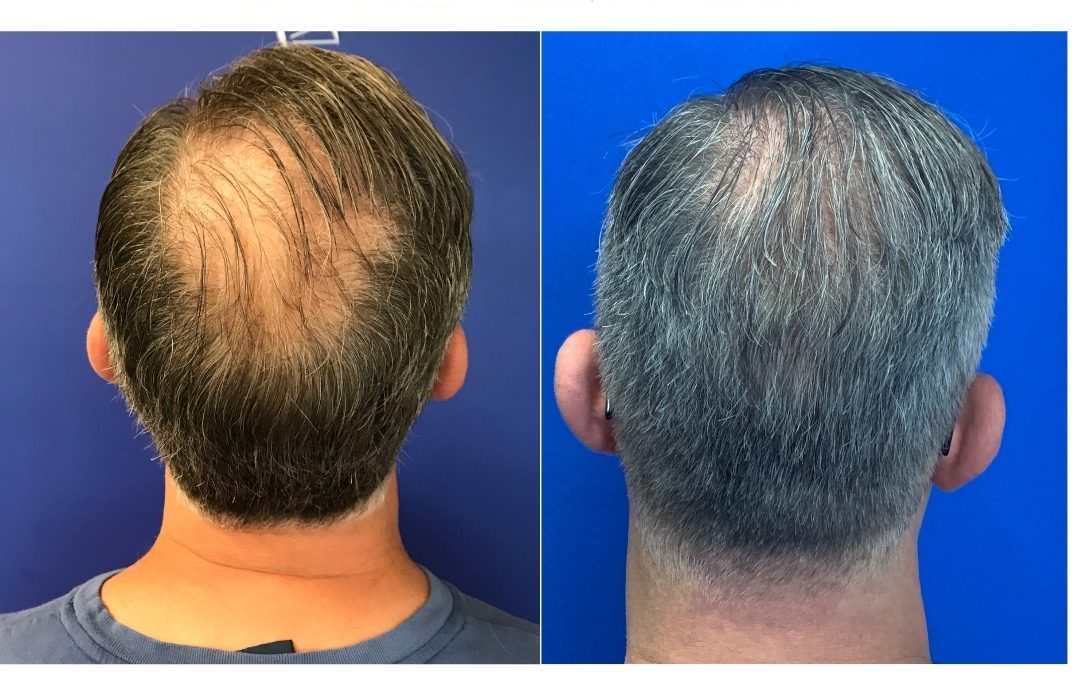
Male pattern baldness (MPB) is a common condition affecting millions of men around the world. It is caused by genetic factors and results in hair thinning and eventually complete baldness on the top of the head.
The good news is that there are various treatment approaches available to help slow down or even stop the progression of MPB. These treatments include medications, topical applications, lifestyle changes, laser therapy, and surgery.
Medications such as Finasteride or Minoxidil can be taken orally or applied directly to the scalp. This type of treatment works by blocking certain hormones from binding to receptors in hair follicles, thus slowing down their miniaturization process resulting in reduced hair loss and possible regrowth for some individuals.
Additionally, changing one’s lifestyle habits like reducing stress levels and eating a healthy diet may also prove beneficial when it comes to managing MPB symptoms over time. Laser therapy uses low-level lasers on affected areas of the scalp which helps stimulate new growth while simultaneously boosting circulation within those areas providing more oxygen and nutrients essential for healthy hair growth/regrowth.
Lastly, surgical options like Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) involve taking donor hairs from other parts of a patient’s body and then transplanting them onto bald patches; this method has proven successful with many patients who have experienced considerable improvement post-surgery although it does require multiple sessions before desired results are achieved
Conclusion
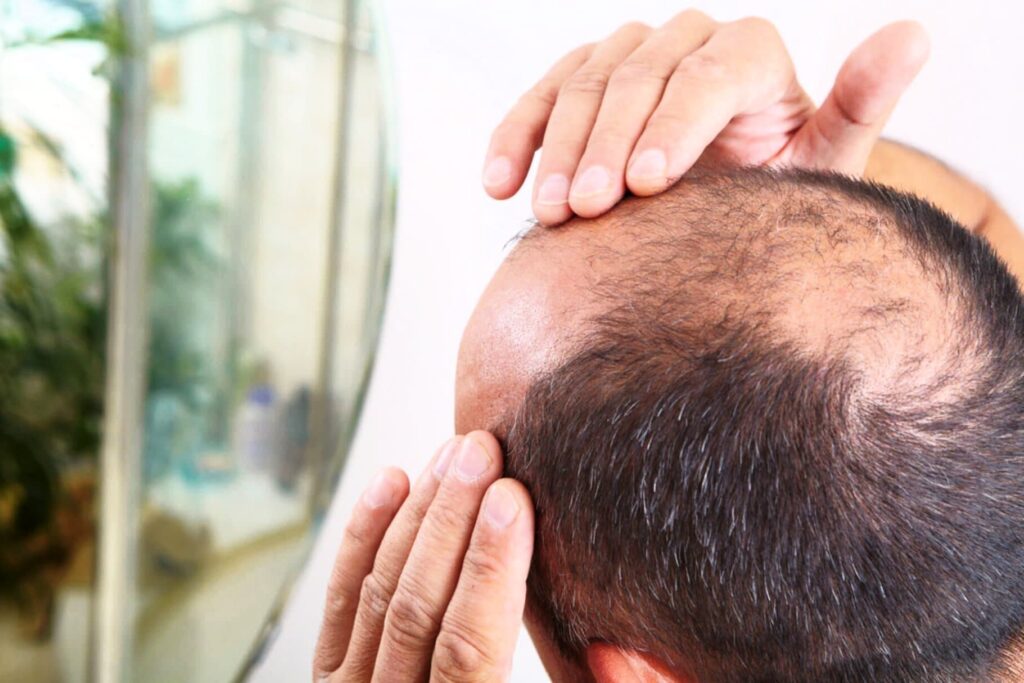
Male Pattern Baldness (MPB) is a common genetic condition that affects millions of men worldwide. It has both physical and psychological impacts, and the search for new treatments continues to be active.
Recent research has identified multiple genes involved in MPB susceptibility, providing an important clue toward understanding its genetic basis. Additionally, many treatment approaches are now available on the market ranging from non-invasive topical therapies to surgical transplants.
While no single approach can guarantee a cure for MPB, utilizing these combined strategies may provide long-term hair regrowth and improved self-confidence for affected individuals.


